32
Artigo Original
Context
COST framework
COST is the longest running European framework
supporting transnational cooperation among research-
ers and scholars across Europe. It is a unique mean
to jointly develop ideas and new initiatives across all
fields of science and technology, through Pan-Europe-
an networking of nationally funded research activities.
Based on an European intergovernmental framework
for cooperation in science and technology, COST has
been contributing, since its creation in 1971, to clos-
ing the gap between science, policy makers and soci-
ety throughout Europe and beyond. It anticipates and
complements the activities of the EU Framework Pro-
grammes, constituting a “bridge” towards the scientific
communities of COST Inclusiveness Target Countries.
It also increases the mobility of researchers across Eu-
rope and fosters the establishment of scientific excel-
lence [1].
COST aims at enabling breakthrough scientific de-
velopments leading to new concepts and products. It
thereby contributes to strengthening Europe’s research
and innovation capacities.
In order to achieve its mission [2], COST endeavours
to:
• Build capacity by connecting high-quality scientific
communities in Europe and worldwide
• Provide networking opportunities for Early Stage
Researchers (ESR)
• Increase research impact on policy makers, regula-
tory bodies and national decision makers as well as on
the private sector.
COST Actions are bottom-up science and technology
networks, open to researchers and stakeholders with a
duration of four years.They are active through a range
of networking tools, such as workshops, conferences,
training schools, short-term scientific missions and dis-
semination activities.
Training Schools aim at widening, broadening and
sharing knowledge relevant to the Action’s objectives
through the delivery of intensive training on a new and
emerging subject [3].
EURNEGVEC
Action
Arthropod vectors and vector-
borne diseases are frequently
zoonotic infections and al-
though their most significant
clinical effects are often on the human population, the
main infection sources are dependent on vectors, animal
reservoirs and environmental factors.Hence, their surveil-
lance and control require efficient and appropriately stand-
ardised methods, integrated knowledge and awareness
among researchers, academics and policy-makers along
with well-trained young scientists [4].
Within the COST Framework, the European Network for
Neglected Vectors and Vector-Borne Infections (EurNeg-
Vec) BMBS COST Action TD1303 was supported from
2014 till 2017.
EURNEGVEC aimed at promoting all of these values and
apply them in the field of vectors (ticks, mosquitoes, sand
flies,midges and fleas) and vector-borne pathogens (virus-
es, bacteria, protozoa and nematodes).
The main objective of the Action was to establish a power-
ful transboundary network of partner institutions across Eu-
rope that were involved in education and research related
to arthropod-transmitted infectious diseases of man and ani-
mals, a network addressing the growing importance of vec-
tor-borne diseases at a time of Global Change, all integrated
under the One Health concept, and reflecting the complex-
ity and demands of current high-end research [5].
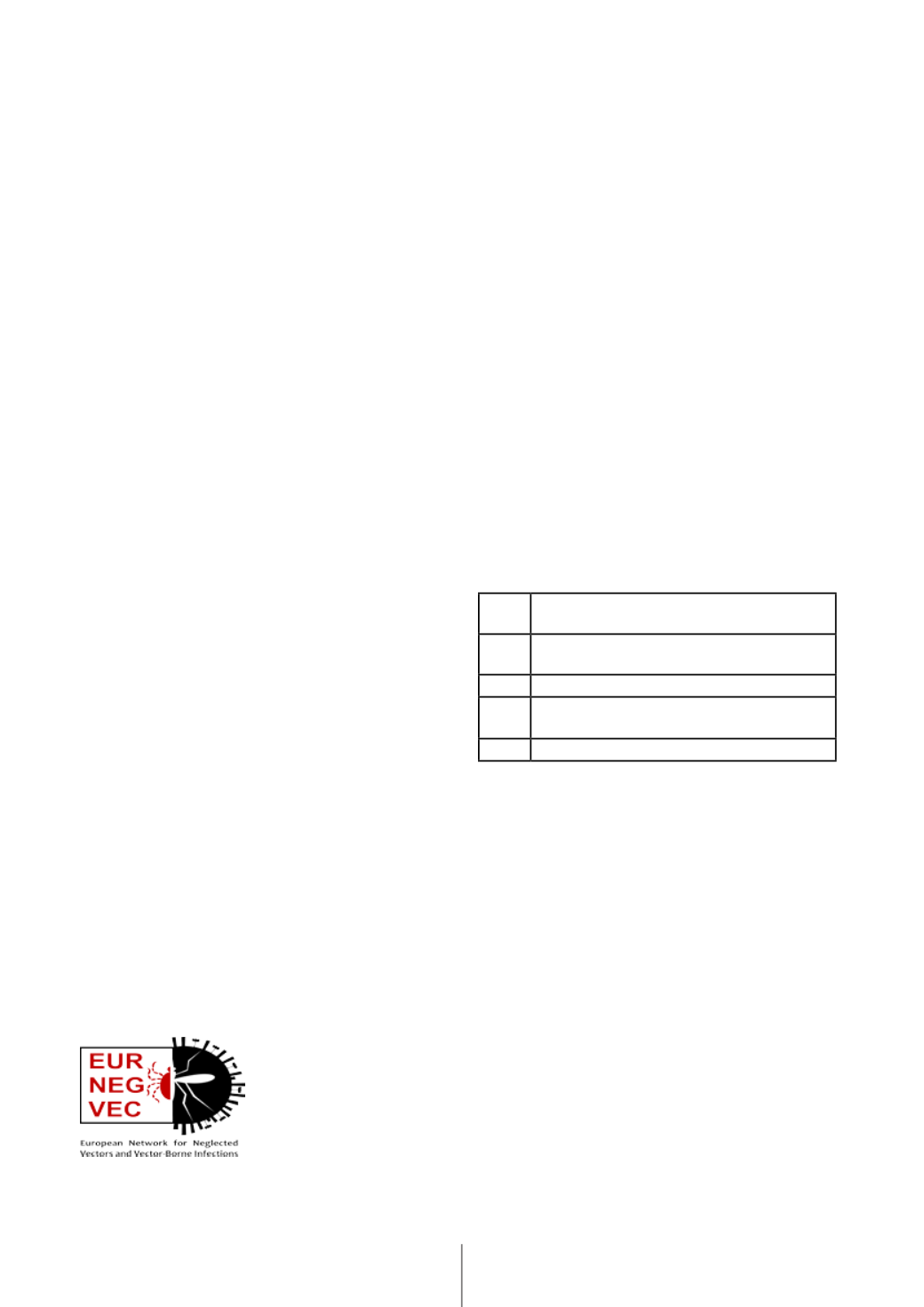
This Action was organized in fiveWorking Groups (WG)
[6]
Three researchers from the IHMT were members of
this Action:Ana Domingos (WG2), Carla Maia (WG1),
and Patrícia Salgueiro (WG2 &WG4).
IHMT/ GHTM
GHTM (Global Health and Tropical Medicine) is a R&D
Centre that congregates IHMT Research.The GHTMmis-
sion is to produce knowledge on global health and tropi-
cal medicine, develop tools and strengthen health systems
through excellence in research, training and systems im-
plementation.Within this mission one of its specific aims
is to reinforce local to global capacity to control vector
borne diseases [7].
The Centre brings together researchers with a track record
inTropical Medicine and International/Global Health and
aims at tackling neglected and emerging diseases under a
multidisciplinary approach, covering aspects from basic
biomedical research to public health policies.
Population genetics and phylogenetics help to understand
WG1
The “One Health” concept in the ecology of vector-
borne diseases
WG2
Barcoding, molecular diagnosis and next generation
sequencing
WG3
Geospatial tools in vector research
WG4
Phylogenetics and phylogeography of vectors and
vector-borne pathogens
WG5
Rare and emerging vector-borne pathogens