Health systems in transition
Portugal
72
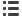
Table 3.6
Provider payment mechanisms
Ministry
of Health
Other
ministries
SHI funds
Private/voluntary
health insurers
GPs
S
Ambulatory specialists
FFS
FFS
Other ambulatory provision
FFS
FFS
Public hospitals
Case payment
Private hospitals
FFS
FFS
Dentists
FFS
FFS
Pharmacies
FFS
FFS
Public health services
S
Social care
PD
PD
Source
: Authors’ own compilation.
Notes
: FFS: fee for service; PD: per diem; S: salary; SHI: social health insurance.
Patients make direct payments to pharmacies, and co-payments by the NHS
may apply depending on the patient’s medical condition and/or financial status
(see sections 3.4.1 and 3.4.2).
Finally, social care included in the National Network of Long-term Care
(RNCCI) is funded by the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Labour,
Solidarity and Social Security, through co-payment to patients.
3.7.1 Paying for health services
Payment of hospitals
Hospital budgets are drawn up and allocated by the Ministry of Health
through the ACSS. At present, public hospitals are allocated global budgets
based on contracts (
contratos-programa
) signed with the Ministry of Health.
Traditionally, budgets had been based on the previous year’s funding, updated
for inflation, but since 1997 a growing proportion is based on DRG information
as well as on non-adjusted hospital outpatient volume. This new activity-based
resource allocation model brought to term research that had begun in the 1980s,
involving systematic DRG grouping and the computation of hospital case-mix
adjusted budgets.
The need to collect data on an individual patient basis for DRG grouping
purposes has led to the generation of a significantly improved information
system for hospitals based on a minimum basic data set –
Folha de Admissão
e Alta
. This basic information system started to be developed in 1989 at the
inception of DRG implementation in Portugal; today it covers all NHS hospitals.
The centralized version of the system, which is run by the ACSS, assists in